Keg Management System
Automation of the keg tracking system includes several stages: assigning a number, keg marking, implementing software and integrating equipment, primary inventory, accounting on the bottling line, accounting in the finished product warehouse, accounting for returns, accounting for service and repairs, monitoring the return dates and irrecoverable losses of KEGs..
Assigning a number
We recommend registering in the global GS1 system and obtaining an enterprise number. To account for returnable containers, this system uses the GRAI (Global Returnable Asset Identifier) number format. This number consists of the enterprise prefix, the asset type number, and the serial number. The company assigns the "property type" categories independently and they can coincide with the numbering adopted at the company before automation.
Keg marking
At this stage, numbers are applied to individual items. Marking is the most expensive stage of automation of KEG turnover accounting, both financially and in terms of time (man-hours). Each unit of container must be assigned an individual number and its reading must be checked by scanners.
The cheapest way is labels with 1D encoding. The barcode contains encoded information about the company, the identification number of the keg type and the identification number of the keg. Based on our experience in automating accounting at enterprises, Vostok specialists recommend using Inotec.de marking with three types of marking for automatic identification. Such marking is more expensive at the initial stage, but fully justifies itself during operation.


Barcode and RFID marking on a self-adhesive base — Inotag Flex on metal SPB. Size 105x35 mm. RFID solution for identifying metal products and equipment, such as kegs for beer and kvass.
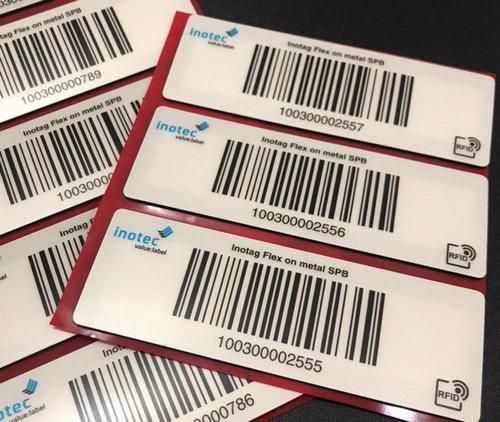

Vostok specialists recommend complex labeling based on Inotag Flex on metal SPB tags. Such complex triple marking contains:
- linear barcode,
- QR code link
- RFID tag.

Using three types of identification allows you to save significant funds on equipping the enterprise with scanners and software for accounting of KEGs. In addition to the enterprise itself, distributors can use the marking and each of them can choose the type of coding for their accounting system. What is most important, against the background of the cost of RFID tags, a linear bar code and QR code are practically free, only the general technological preparation is paid for.
KEG laser marking
This type of direct keg marking can be used both after primary marking with labels and as primary marking. The advantages of laser keg marking include reliability (this type of marking is difficult to remove even with mechanical tangles), as well as the absence of costs for consumables. Having equipped the enterprise with a laser marker, you can apply the coding yourself. If the kegs are laser marked at the second stage, then a label with a linear 1D code is used as the main identification medium, and 2D laser coding is used to restore the label during keg repair.

For laser marking of kegs, it is recommended to equip the unit for simultaneous application of 2 codes on the top and bottom of the kegs with duplication of the QR code with numbers. If for some reason scanning the code is difficult, the accounting operator can enter the numbers manually. As a rule, kegs are loaded into the marking unit manually. The marking time itself is 20-30 sec. depending on the lasers used. The total cycle time for 1 keg is about 1 minute — loading, marking, checking, unloading.

In this case, the main accounting is carried out using bar codes, and RFID tags provide shadow contactless control at checkpoints.

Inventory
After kegs are marked with bar codes, an inventory is taken and the information is entered into the database using data collection terminals. After the inventory, there is acceptance to the warehouse, warehouse accounting and issue from the warehouse.

At the warehouse, the bar code is read by the data collection terminal and information about the accepted or issued products is transmitted to the accounting system database. When kegs are returned to the warehouse, the bar code must be read. Thus, the data on the return of kegs is entered into the accounting system of the enterprise. Most often, such a system is the «1C: Enterprise» program.
Software
Software is installed on data collection terminals, which connects to the enterprise accounting system database and provides information about the keg: to whom and when it was shipped, when it was returned, when it was last repaired. Keg control points equipped with RFID tag readers are connected to the accounting system via RFID server software.
Keg control points
- Bottling shop
- Plant warehouse
- Distributor warehouse
- Point of sale
Benefits of implementing the system
- Reduced likelihood of keg disappearance.
- Tracking the movement of kegs from the moment of shipment to the customer until the moment of return.
- Control of keg damage and repairs.
- Service operations — when the repair was done and what was repaired.
- Reduction of operating costs.
- Ability to collect and analyze data on the condition of containers, turnover and "stuck" kegs.
- Timely detection of the end of the keg service life.