Barcode system in manufacturing
Manufacturing enterprises often encounter problems with the mismatch of raw materials, parts and components, lack of control over purchased (incoming control) and manufactured products (quality control). Organizing full-fledged tracking of product output with constant quality and quantity control at each stage of production is a rather difficult task.
Using bar codes (or QR) and automated identification, you can solve the problem of quality and quantity control, as well as ensure production tracking at all stages and sites without increasing the number of employees. Employees perform all accounting and control operations in the background by scanning bar codes on documents (production tasks), raw materials (incoming control labels), containers, equipment, blanks, storage locations. Information is generated almost online, which ensures not only control over the execution of operations, but also full-fledged dispatching with the ability to control the timing of work operations.
They brought the wrong thing, assembled it incorrectly, it was a mix-up, it broke down, the state of the work, the fact of manufacturing a part or unit - most of these problems can be solved by tracking parts by bar codes. The level of detail (depth) of tracking is determined for each enterprise individually. First of all, identification by bar codes significantly reduces the "human factor", and the speed of the enterprise and the execution of work increases.
Fewer errors - more speed. When implementing barcoding, at a minimum, it is guaranteed that you can eliminate manual data entry errors and errors in rewriting data multiple times from logs or spreadsheets.

Barcoding in production can be used very widely. In addition to the usual application of bar codes to goods for product identification, bar coding can be used for the following purposes:
- inventory (lots and series);
- document identification automation;
- employee passes;
- job cards;
- storage locations (cell accounting),
- production operation cards;
- product serial numbers;
- library cards;
- production and transport packaging;
- property identification (fixed assets), etc.
Document identification
A barcode on documents allows you to automate document flow, generate documents based on other documentation, simplify the search for documents in the database, and track their movement.
The use of barcodes and scanners allows us to reduce the number of manual operations, significantly reduce the time required to process documents and, naturally, the number of errors.
Ideally, employees of the enterprise should not communicate verbally on production tasks, and all processes occur “on the basis”: based on the production plan, production tasks are printed out in the workshop (an example is the use of a kitchen printer in a restaurant), as soon as a production employee receives the task, reads and understands it — he scans the barcode and the manager sees that the task has been accepted for production.
By scanning the task barcode, the employee initiates related processes, such as weighing raw materials (weighing act), receiving components (request to the components warehouse).
This way, a document tree is formed, and it is possible track the stages of order production.

Employee pass
Currently, several technologies are used to identify employees at checkpoints - RFID, magnetic stripe and barcode. Each of these technologies has its advantages and disadvantages. The advantage of barcode technology is the price: Barcode scanners are significantly cheaper than RFID readers.
Login to the accounting program using an employee pass.
Also, using a pass with A bar code is convenient if several employees use one workstation.
For example, a team of order pickers receives tasks on one PC: each employee scans their pass and receives a printout with an individual task. Another example of teamwork on one PC from our practice is a laboratory. When performing laboratory tests, employees work with different equipment, then, as they complete the work, they enter data on a common PC "Laboratory Operator". The laboratory technician scans their personal card and analysis form. In this way, a personal chain of documents and electronic journals are formed. Laboratory automation based on barcodes allows to save time significantly and simplify journal keeping and document flow.
Job cards
One employee can perform several functional duties of different positions. In addition, one employee can replace another during the absence of the latter due to illness or vacation. Job cards with a barcode are used to identify the employee in the system and select a role (program interface). In our enterprise automation projects, job cards were successfully used both at newly created enterprises, where business processes are just being debugged, and at enterprises with established business processes. For newly created enterprises, the use of job cards for working with the program and interface is a vital option, since it allows to avoid many growth problems. An employee working in several positions (the norm for new enterprises), having trained a colleague, hands him a job card and job instructions. The job card option allows you to debug automated workstations (AWS) on the site manager's PC and then distribute them among operators.
Storage locations
Marking of storage locations with tags with bar codes Allows to automate the accounting of documents on placement, collection of orders, as well as inventory in warehouses. The placed products are "assigned" to a storage location. This is done very simply and quickly: the storekeeper scans the bar code on the product or its packaging, and then the storage location code. Information on the placement of products is saved in the accounting system. When a task arises to collect an order, the employee receives a task already indicating the storage locations.
Operation map
It is very convenient to use barcode operations for repetitive actions. The command barcode code can be located not only on the map. It can be printed in the production order, located next to the equipment, on the stand, container, machine. In this case, the employee does not need to automatically switch to working on the keyboard. Operations can be anything: container, document holding, document saving, label printing, document printing, as well as gate opening. Below are photos of how the problem of equipment failure was solved using the operation barcode — weighing terminals.

Frequent pressing of the "tare" button caused the scale keys to go deeper. At the same time, the operator used a scanner to count the products. Vostok LLC specialists added the "tare" operation code and everything worked out! The worker does not need to make unnecessary movements, he does everything with a barcode scanner. Contactless taring of scales solved the problem of their removal from the building.
<р>
Operation code for control weighing devices. The number of weighings at large enterprises, frequently pressing the "tare" button leads to failure of the scale keyboard and even the weighing processor itself.

Using a command barcode, control the reduction of "tare" contactless.

Serial numbers
Serial numbers in production allow for virtually the entire production cycle to be controlled: from the launch of production to the provision of warranties and service, and in some cases, even disposal. Both linear 1D codes and 2D codes of printed or direct marking are used for serial numbering. In some cases, only 2D marking is possible. Electronic components and small parts are marked using direct marking (DPM) by impact or laser application.

Special DPM 2D Scanners are used to read direct markings.
For reading direct marking, special DPM 2D scanners are used.

Card files
Marking card files with barcode labels allows for automation of work with cards and a smooth transition from paper documents to electronic ones.

Production and transport containers
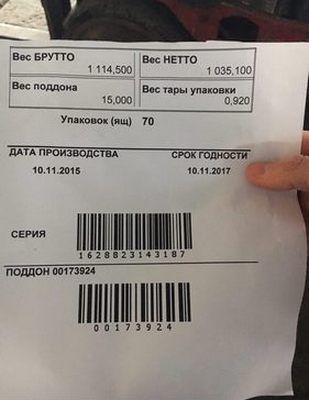
Marking production and transport containers with bar codes makes it possible to automate the accounting of container turnover. In addition, it allows identifying ordered goods transported in this container, calculating the weight of the container when determining the mass of the product.

A wide-format and high-performance label printer is used to label the pallets. The printer is integrated into the enterprise's accounting system, which allows each pallet to be labeled with a unique collective label containing all the data on the cargo collected on the pallet.

Wide-format printer TSC TTP-2610MT.
In addition to the barcode, the following are used to automate the identification of containers: RFID tags.
Inventory of property
Marking property and fixed assets with numbers and bar codes allows you to automate the collection of data on property using data collection terminals and specialized software.

Barcode standards
Standardization and assignment of barcodes is carried out by the organization GS1. This is an international organization that assigns coding according to international standards: GTIN is an international product code, SSCC is an identification in supply and transport processes, GDTI is a document type ID, GIAI is for property identification.